Our breast implant surgery in Turkey has become a favorite choice for international travelers seeking expert care and transformative results. With cutting-edge techniques and experienced surgeons, our clinic provides augmentations that enhance body proportions, restore lost volume, and improve symmetry.
Take the first step today by contacting us for a breast augmentation consultation. You’ll get to discuss your needs with someone who can answer all your questions and book your procedure. Keep reading to learn more about having your procedure in Turkey, what to expect, and more.

Why the Breast Area Matters
The breast area plays a key role in body symmetry, femininity, and self-confidence. For many women, breast size and shape can influence how they feel about their overall appearance. Some may naturally have smaller breasts, while others experience volume loss after pregnancy, breastfeeding, or significant weight loss. Enhancing the breasts through augmentation can restore balance to the body’s proportions and boost self-esteem.
Causes of Small or Uneven Breasts
Several factors can influence breast size, shape, and symmetry, often motivating women to consider augmentation:
- Genetics: Breast size is largely hereditary, meaning naturally smaller or uneven breasts can run in families.
- Hormonal changes: Shifts during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause may affect breast development and volume.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Many women lose breast fullness or experience sagging after nursing.
- Weight fluctuations: Significant weight loss can result in reduced fat tissue in the breasts, leading to a smaller or less firm appearance.
- Aging: Over time, skin loses elasticity, and breasts may lose volume, appearing flatter or less youthful.
- Trauma or surgery: Injury or medical procedures, such as tumor removal, can alter breast shape or size.
Why Choose Breast Augmentation in Turkey?
Turkey has become a popular destination for breast augmentation procedures, offering world-class medical facilities, highly skilled surgeons, and affordable pricing. With its blend of cutting-edge technology and personalized care, Turkey attracts patients from around the world seeking quality aesthetic surgery.
The cost of breast augmentation in Turkey is often significantly lower than in many other countries, without compromising on quality or safety. Many clinics also provide all-inclusive packages that include accommodation, airport transfers, and even postoperative care.
Additionally, Turkey’s unique location offers the opportunity to combine your surgery with a memorable vacation. Cities like Istanbul, known for their rich history and vibrant culture, provide an ideal backdrop for recovery and relaxation.
Breast augmentation surgery in Turkey is commonly performed alongside procedures like a Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL) and a tummy tuck for a comprehensive body contouring approach. Breast augmentation enhances the chest, a BBL adds volume and shape to the buttocks, and a tummy tuck sculpts and firms the abdomen. Together, these surgeries help achieve a balanced and proportionate look. Discover more about BBL surgery in Turkey and tummy tuck surgery in Turkey.
Types of Breast Augmentation Techniques
Breast augmentation can be performed using different techniques, each offering unique benefits depending on the patient’s goals and body type. The most common method is implant augmentation, where silicone or saline implants are placed either beneath the breast tissue or under the chest muscle. This technique allows for a predictable increase in size, with a wide variety of shapes and sizes to choose from, though it does carry risks such as implant rupture, capsular contracture, or the possibility of needing replacement surgery in the future.
Another option is fat transfer augmentation, which involves harvesting fat through liposuction from areas like the abdomen or thighs, purifying it, and then injecting it into the breasts. This method provides subtle, natural-looking results and avoids the use of foreign material, but it is more limited in the amount of volume it can add, and some of the fat may be reabsorbed by the body over time, making the results less predictable.
A newer approach is hybrid augmentation, which combines implants with fat transfer. Implants provide the desired core volume, while fat grafting enhances the cleavage, contours, and symmetry of the breasts. This method delivers a fuller yet natural appearance and allows for a high degree of customization. However, it typically requires a longer procedure, involves higher costs, and carries the risks associated with both implants and fat transfer.
Breast Augmentation Surgery
Before The Operation
Before surgery, you will have a consultation with your doctor to assess your body proportions and discuss your expectations. Together, you will choose the most suitable procedure. In cases of breast sagging, a breast lift may be combined with breast augmentation to achieve a fuller and lifted appearance. Breast lifting can often be done during the same surgery, but in some cases, a separate procedure may be required. Your plastic surgeon will guide you through this decision.
The doctor will also conduct appropriate medical tests to ensure you are ready for surgery.
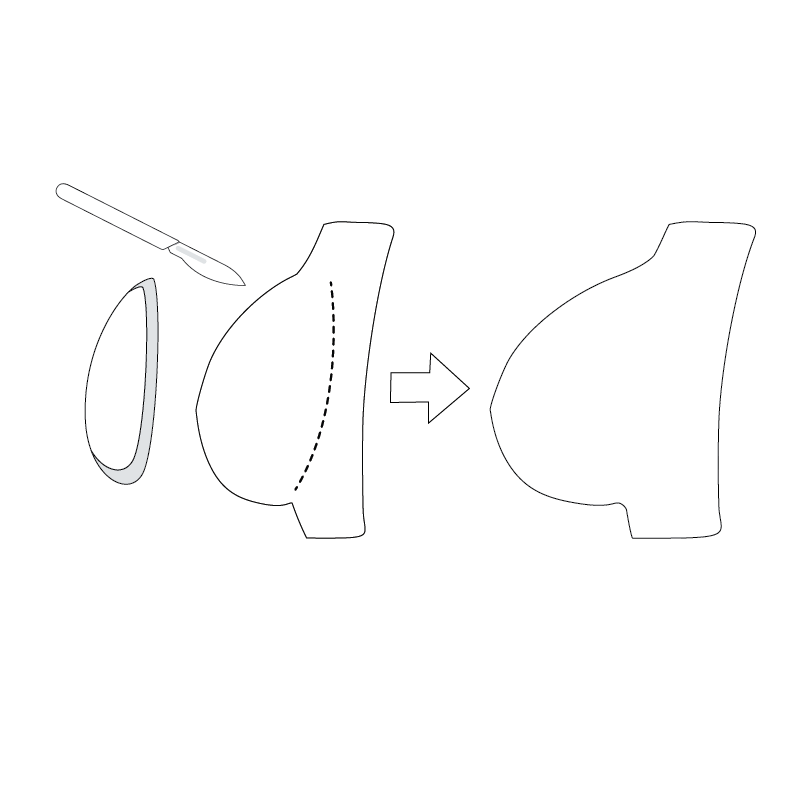
During The Operation
Breast augmentation surgery in Turkey is performed under general anesthesia and typically takes 1 to 1.5 hours.
If the option chosen is fat transfer, the surgeon will remove fat from areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or flanks using liposuction. The fat is then processed and injected into the breasts to achieve the desired size and shape.
For breast implants, the surgeon makes an incision, creates a pocket in the chest or breast area, and places the implant in one of the following positions:
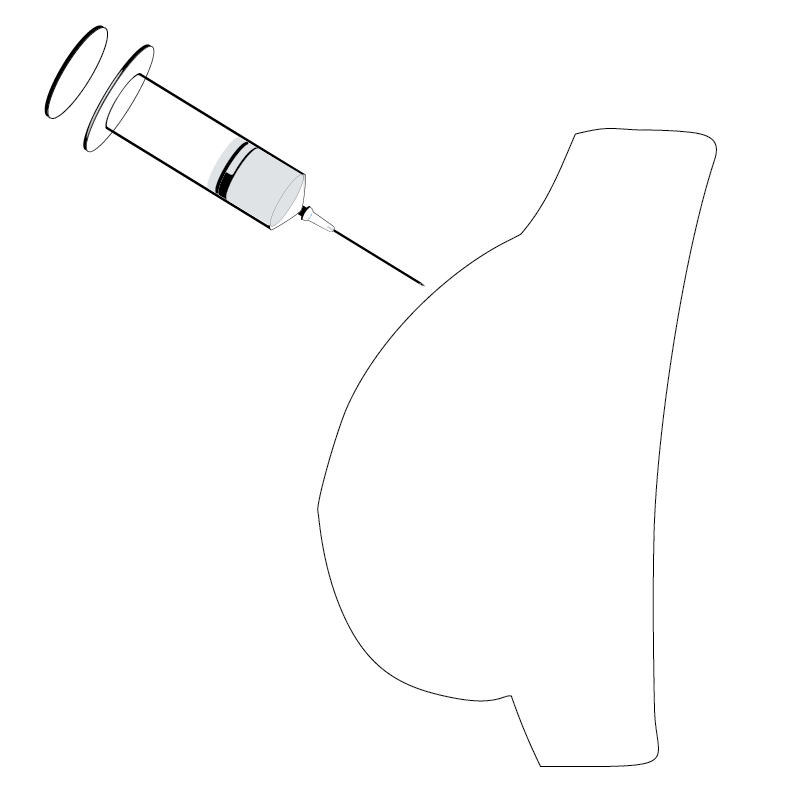
- Underneath the pectoral muscle, between the breast tissue and the chest wall.
- On top of the pectoral muscle, beneath the breast tissue.
Incisions may be made in one of four locations:
- Transumbilical: In the navel.
- Inframammary: Beneath the breast, just above the crease.
- Transaxillary: Near the armpit, where the arm meets the chest.
- Periareolar: Around the lower edge of the areola.
After The Operations
Following breast augmentation, patients can usually return home the same day. Mild swelling, tightness, and discomfort are common at first but improve within days. A supportive bra is worn to aid healing, and most people return to work within a week. Strenuous activity should be avoided for several weeks while the breasts gradually settle into their natural shape.

Benefits of Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation offers both aesthetic and psychological advantages, helping women feel more confident and satisfied with their appearance. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced volume and shape: Implants or fat transfer can restore or increase breast size, creating fuller, rounder contours.
- Improved symmetry: Many women have naturally uneven breasts, and augmentation helps achieve a more balanced look.
- Youthful appearance: The procedure can rejuvenate the chest area, especially after pregnancy, breastfeeding, or aging.
- Clothing fit: Clothes, swimwear, and lingerie often fit better and feel more flattering with enhanced proportions.
- Boost in self-confidence: Many women report feeling more feminine, attractive, and comfortable in their own skin.
- Long-lasting results: With proper care, implants can provide years of satisfaction before requiring replacement or adjustment.
Breast augmentation is more than just a cosmetic change: it can significantly improve quality of life and self-image.
Risks of Breast Augmentation
Like any surgical procedure, breast augmentation comes with potential risks and complications that should be carefully considered before making a decision. Common risks include:
- Infection or poor healing: Though rare, infections or delayed healing may occur around the incision site.
- Capsular contracture: Scar tissue can sometimes tighten around the implant, causing hardness or distortion.
- Implant complications: Risks include leakage, rupture, or displacement, which may require revision surgery.
- Changes in sensation: Some patients may experience temporary or permanent numbness in the nipple or breast area.
- Asymmetry or dissatisfaction: Results may not perfectly match expectations, and revision surgery could be necessary.
- General surgical risks: Bleeding, anesthesia-related issues, or blood clots are possible, as with any surgery.
While most patients recover smoothly and enjoy their results, being aware of these risks ensures realistic expectations and informed decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does Breast Augmentation Surgery Cost in Turkey?
The cost of breast augmentation varies depending on the technique used, the type of implant, and the areas involved. Prices may also change if the procedure is combined with other surgeries. It’s best to consult your surgeon for detailed pricing.
What Types of Breast Implants Are Available?
- Saline Breast Implants: Filled with sterile salt water. If the implant leaks, the saline is safely absorbed and expelled by the body. These are FDA-approved for women aged 18 or older.
- Structured Saline Implants: These have a more natural look due to their internal structure.
- Silicone Breast Implants: Filled with silicone gel, offering a more natural breast tissue feel. Recommended for women aged 22 or older.
- Gummy Bear Breast Implants: These maintain their shape, with a fuller bottom and tapered top.
- Round Breast Implants: Provide a fuller and larger appearance.
- Smooth Breast Implants: Offer a soft and natural feel.
- Textured Breast Implants: Develop scar tissue that adheres to the implant, reducing movement and repositioning.

Who is a Good Candidate for Breast Augmentation?
You may be a good candidate for breast augmentation if:
- You are in good health.
- You are not pregnant or breastfeeding.
- You feel that your breasts are too small.
- Your breasts are asymmetrical.
- One or both breasts failed to develop normally.
- The upper part of your chest appears empty.
Breast Augmentation Surgery in Turkey: Before and After
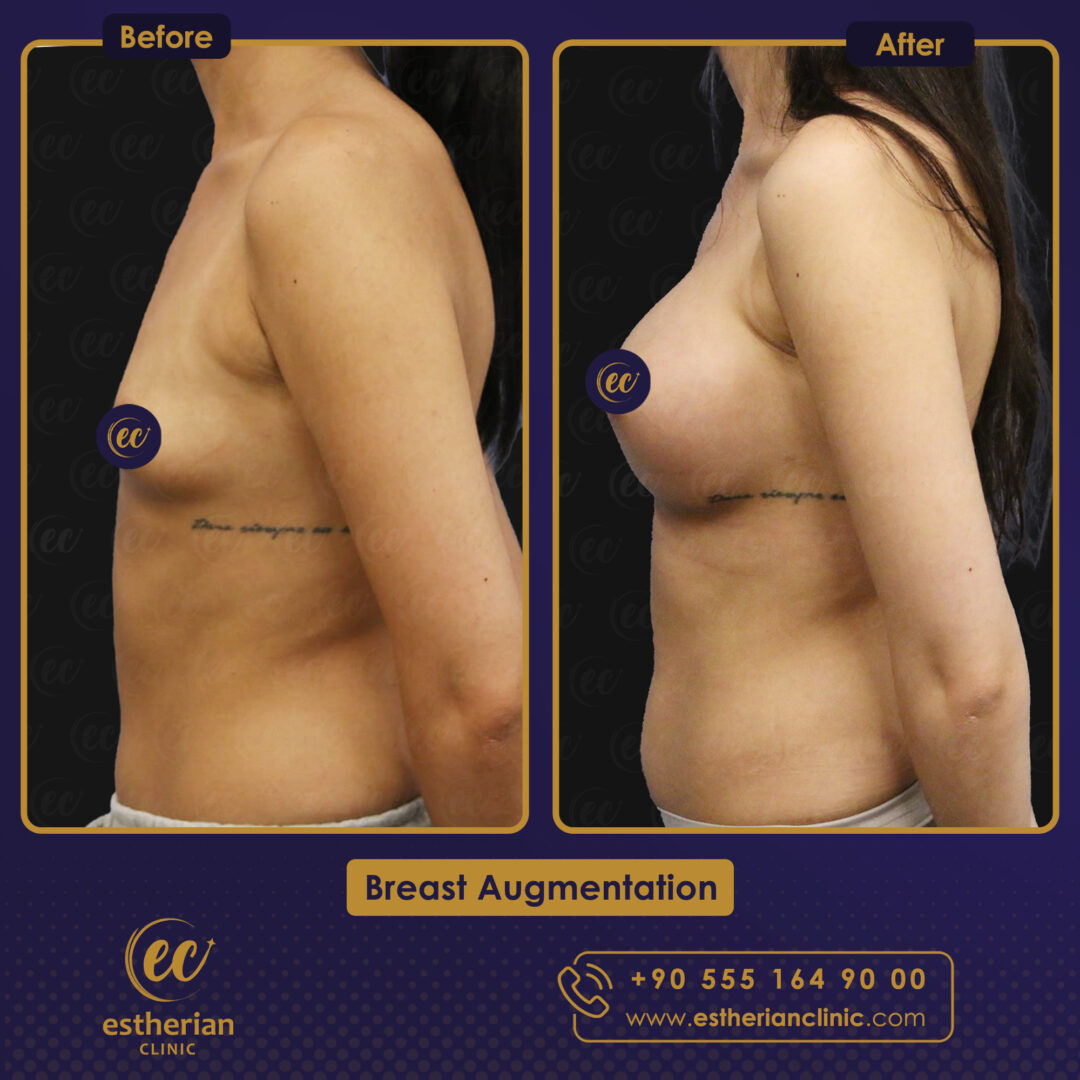
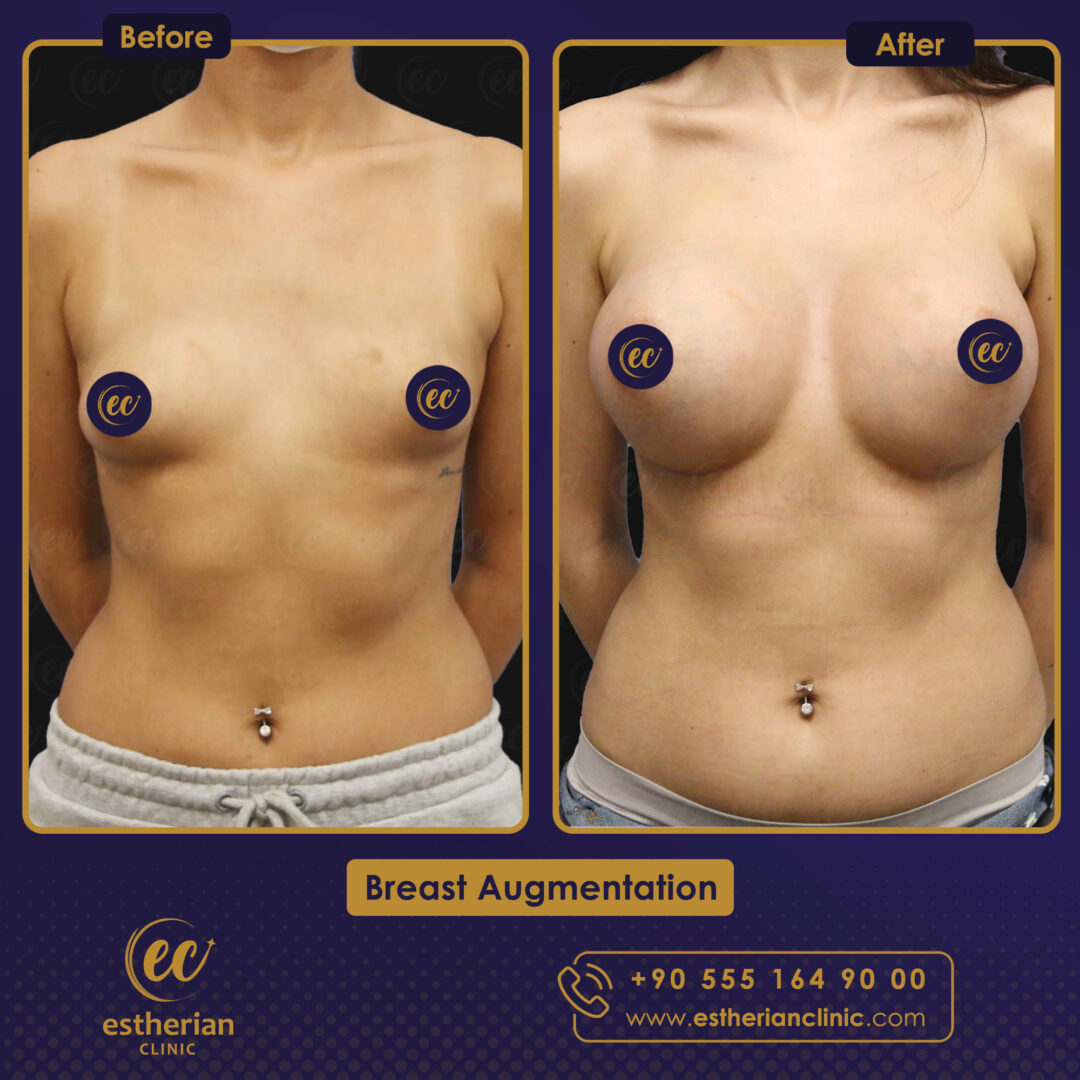
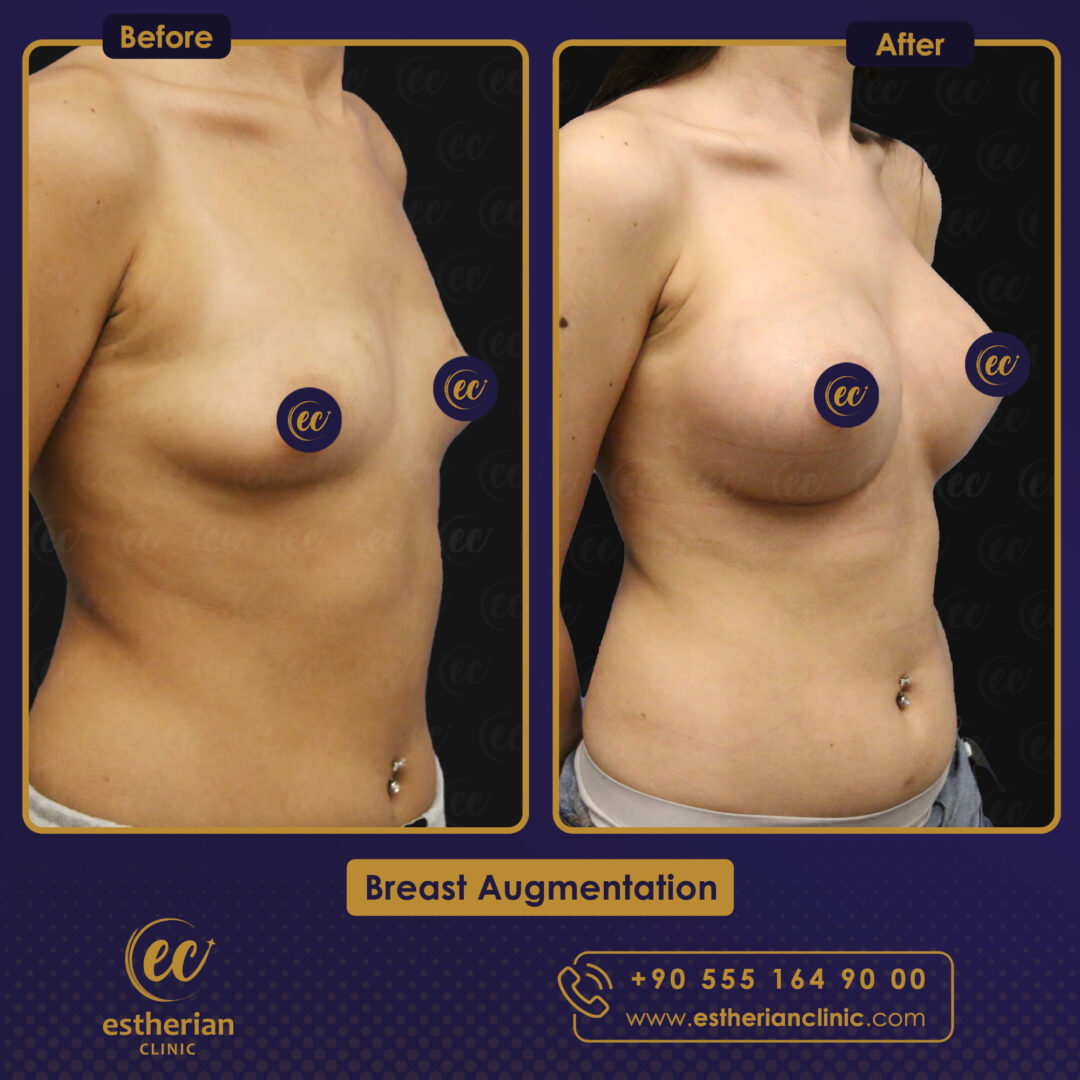
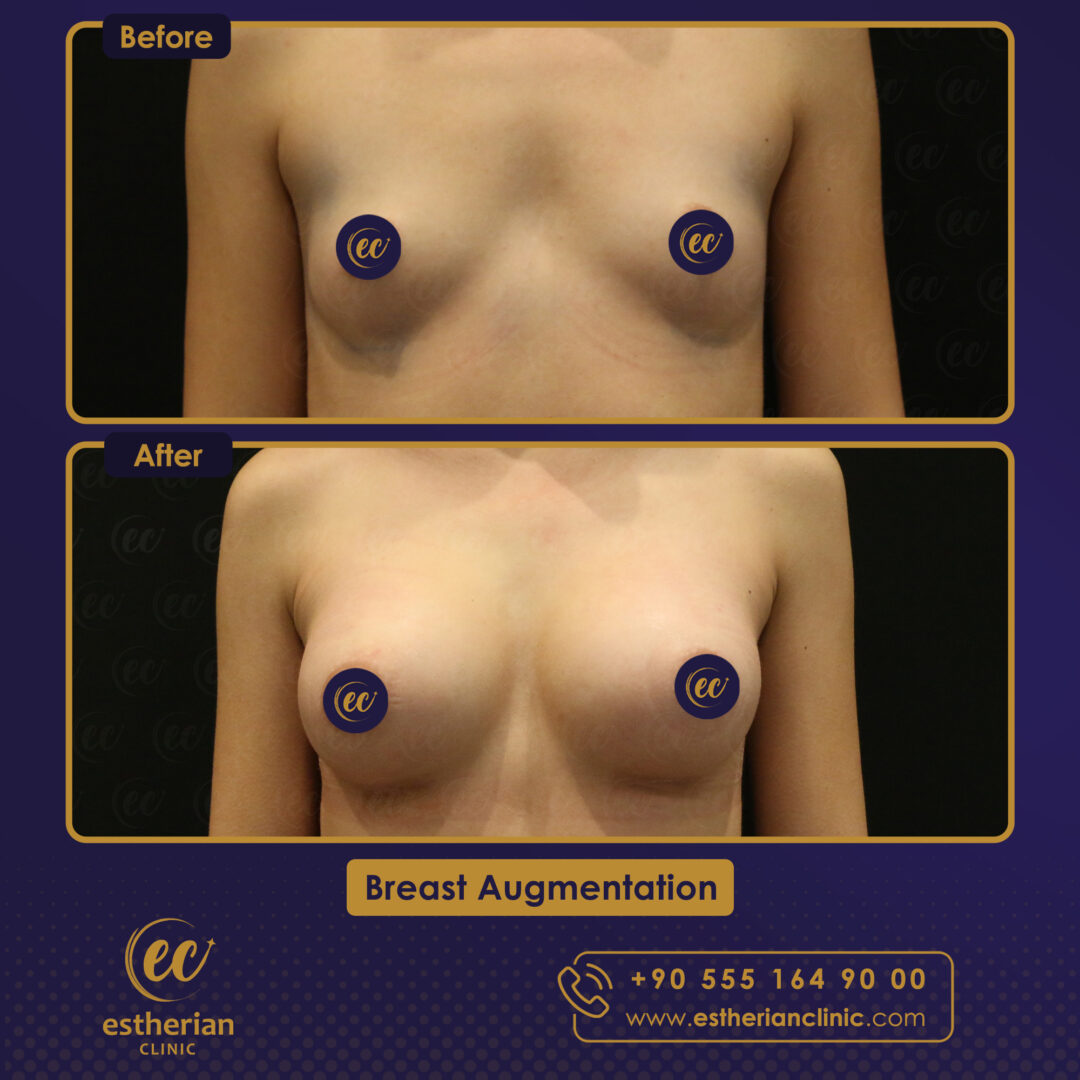
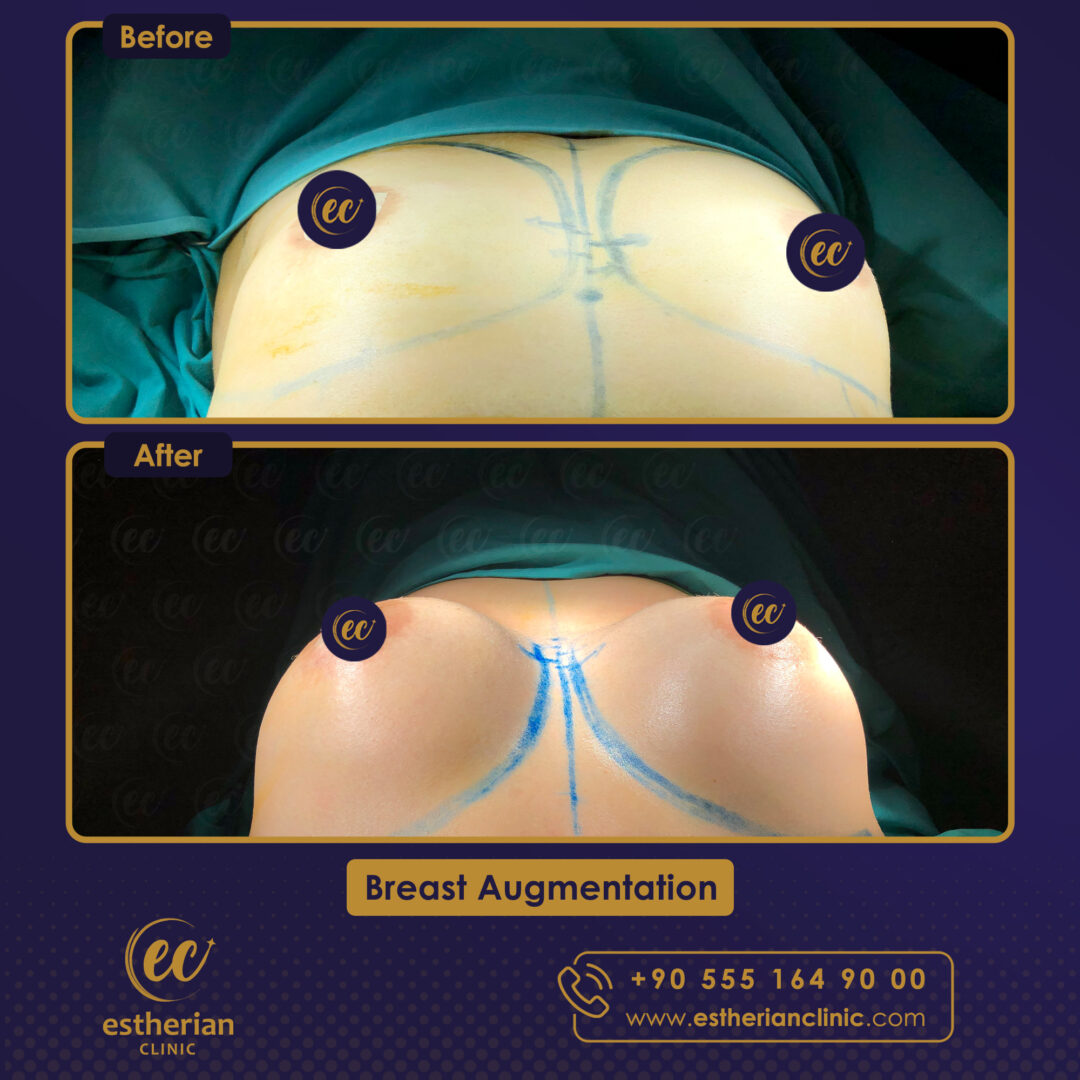
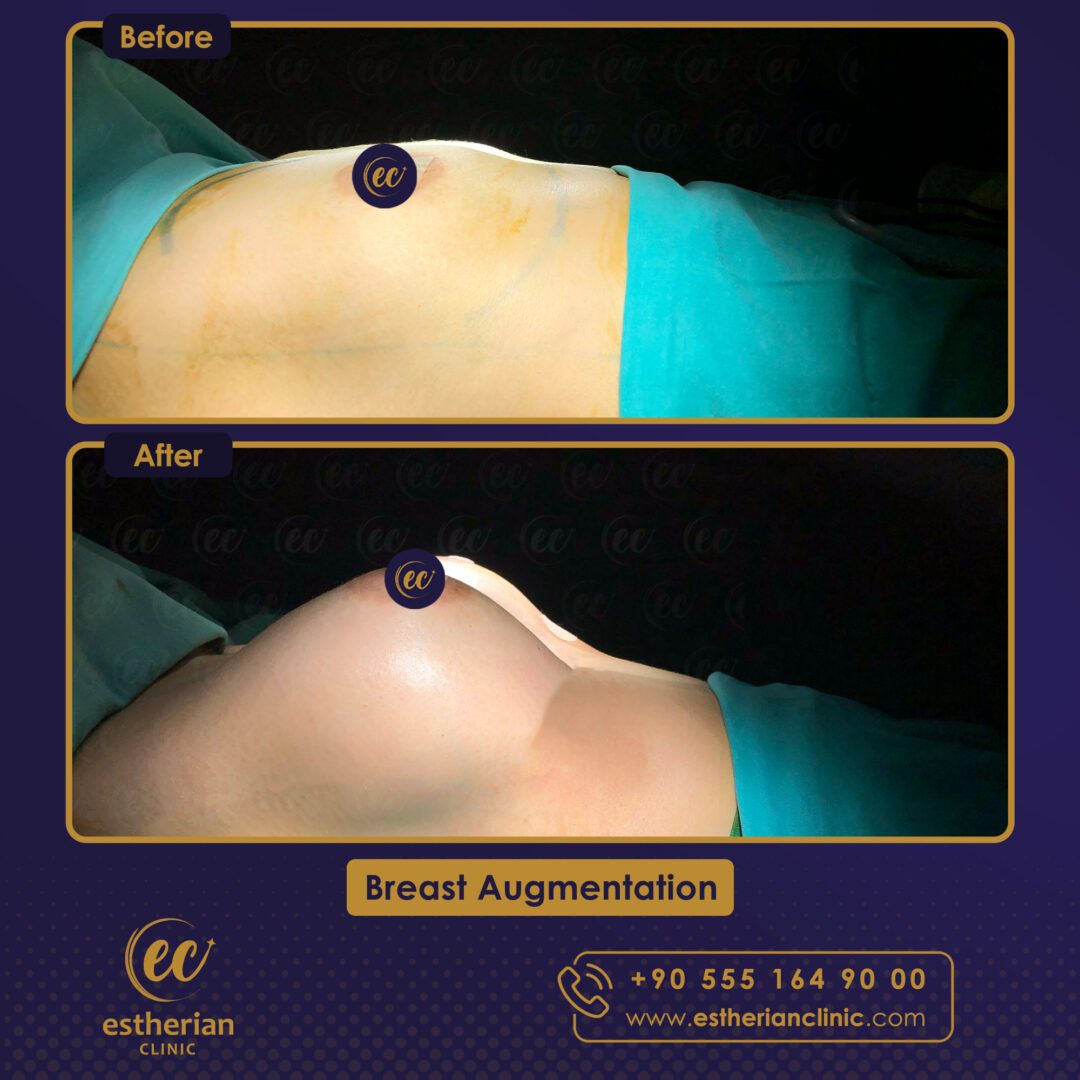
Related Article About Breast Augmentation Surgery In Turkey
Realself: “5 Things to Know About Choosing the Right Breast Implant Size”

