Otoplasty surgery in Turkey is a popular procedure designed to improve the appearance of the ears by reshaping, resizing, or repositioning them for a more balanced and natural look. Whether you want to correct prominent ears or address other aesthetic concerns, Turkish clinics provide expert care with advanced techniques. Renowned for its combination of quality and affordability, Turkey has become a leading destination for otoplasty surgery. This effective solution can help transform your confidence!
Why the Ear Area Matters
The ears may seem like a small feature, but they play a major role in framing the face and influencing overall facial balance. When ears are overly prominent, asymmetrical, or disproportionate, they can draw unwanted attention and affect a person’s confidence from a very young age. Children, in particular, are often teased about their ears, which can lead to self-esteem issues that carry into adulthood.
Correcting ear shape or position with otoplasty offers more than just cosmetic improvement. It creates harmony between the ears and other facial features, allowing the focus to remain on the eyes, smile, and other defining aspects of the face. For many patients, otoplasty is a life-changing procedure that provides a boost in confidence, whether it’s performed during childhood or later in life.
Causes of Prominent or Misshapen Ears
Understanding why ears appear prominent or irregular is essential for planning an effective surgical approach. The most common causes include:
- Genetics: Ear shape is highly hereditary. Children often inherit ear prominence or irregular cartilage structures from one or both parents.
- Cartilage Structure: Underdeveloped folds (antihelical folds) or enlarged conchal bowls often cause ears to protrude.
- Earlobe Size: Genetics influence earlobe dimensions, which may also be corrected during surgery.
- Congenital Conditions: Birth defects like microtia or lop ear deformity can lead to irregular ear shapes.
- Injury or Trauma: Injuries in infancy or later in life can alter cartilage growth, leading to asymmetry.
While many adults seek otoplasty for cosmetic reasons, children often undergo surgery to avoid teasing and improve self-esteem at an early age.
Types of Otoplasty Techniques
Otoplasty techniques are tailored to each patient’s unique needs and ear structure. Surgeons carefully evaluate factors like ear cartilage shape, ear prominence, and overall facial balance before selecting the best approach.
- Traditional Ear Pinning (Setback Otoplasty):
This is the most common otoplasty technique, designed to pin back ears that protrude too far from the head. The surgeon reshapes or folds the cartilage using sutures to create a more natural contour. Incisions are typically hidden behind the ear, making scars virtually invisible. - Cartilage Scoring or Reshaping:
For patients with stiff or thick cartilage, the surgeon may use precise scoring techniques to weaken and reshape the cartilage. This allows for permanent repositioning and a smoother ear appearance. - Incisionless Otoplasty:
A minimally invasive option, incisionless otoplasty uses internal sutures placed through tiny punctures in the skin. This approach is ideal for patients with mild ear prominence, offering a shorter recovery time and virtually no visible scarring. - Ear Reduction Surgery (Macrotia Correction):
When ears are disproportionately large, excess cartilage or skin can be removed to achieve a smaller, more proportionate shape. This technique focuses on both size and positioning for balanced results. - Earlobe Reshaping:
Otoplasty can also correct stretched, torn, or enlarged earlobes. This is a popular choice for individuals with earlobes affected by heavy earrings, aging, or injury.
These techniques can also be combined for comprehensive results, ensuring that both ear size and position complement the patient’s overall facial harmony.
The Otoplasty Procedure
Before The Surgery
Before the surgery, the surgeon conducts a thorough medical examination to ensure the patient is in good health and can safely undergo the operation. Smoking is strongly discouraged before the procedure, as it can interfere with healing. Patients are also advised to avoid aspirin and anti-inflammatory medications, which can increase bleeding during and after surgery.

During The Operation
During the operation, anesthesia is administered according to the patient’s specific needs. Options include local, intravenous sedation, or general anesthesia, with the surgeon guiding the patient to choose the most suitable option. Incisions are typically made on the back surface of the ear to minimize visible scarring. When incisions are necessary on the front of the ear, they are discreetly placed within the natural folds to remain hidden. The ear cartilage is reshaped and secured with internal, non-removable sutures, creating a natural and symmetrical contour.
After The Surgery
Care is essential to ensure a smooth recovery. Patients are advised to rest with their heads elevated to reduce swelling and edema. A protective bandage is usually applied to maintain the new shape and protect the ears during the healing process.

Ideal Candidates for Otoplasty
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for otoplasty. This procedure is most effective for individuals in good overall health with realistic expectations. Children as young as five years old can undergo otoplasty because their ear cartilage is typically stable enough for correction at that age. Non-smokers generally heal better, making them ideal candidates. Additionally, candidates should be able to clearly express their feelings about the procedure and demonstrate a willingness to follow post-surgery instructions.
Benefits of Otoplasty
Otoplasty offers more than just aesthetic improvements—it can have a profound impact on self-image, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Facial Harmony
By reshaping or repositioning the ears, otoplasty creates better facial balance and proportion. This subtle change allows your natural features—like your eyes and smile—to stand out, rather than your ears. - Boosted Confidence and Self-Esteem
For many, prominent or misshapen ears have been a lifelong source of insecurity. Correcting this concern often leads to a dramatic improvement in self-confidence, allowing individuals to feel more comfortable in photos, social settings, and professional environments. - Early Correction for Children
Otoplasty is one of the few cosmetic procedures recommended for children as young as five. Addressing ear concerns early can prevent teasing, bullying, and the emotional distress that can come with growing up feeling self-conscious about appearance. - Natural-Looking Results
Modern techniques ensure scars are discreetly hidden and the final shape of the ears looks natural and proportionate. Skilled surgeons focus on preserving a soft, natural contour rather than an overly “pinned back” look. - Permanent Results
Unlike some cosmetic procedures that require ongoing maintenance, otoplasty typically provides permanent results. Once the ears are repositioned and cartilage is reshaped, the improvements last a lifetime. - Minimal Downtime
Otoplasty is generally a straightforward outpatient procedure with a relatively quick recovery period, making it easy to fit into busy lifestyles.
Risks of Otoplasty
While otoplasty is considered a safe and effective procedure, it’s important to understand that all surgeries carry some level of risk. Being informed helps patients feel prepared and confident when making decisions. Potential risks include:
- Unsatisfactory Results
While most patients are highly satisfied, there’s always a chance the final results may not meet expectations. Revision surgery is an option in these rare situations. - Anesthesia-Related Complications
As with any procedure requiring anesthesia, there’s a small risk of complications. Surgeons carefully evaluate your medical history to minimize these risks. - Asymmetry Between Ears
Surgeons strive for symmetry, but slight differences between ears may occur, even after healing. In rare cases, minor revisions can be performed to achieve a more balanced appearance. - Bleeding and Hematoma Formation
Bleeding under the skin can cause swelling or discomfort. Compression bandages and careful monitoring after surgery help prevent these complications. - Infection at the Surgical Site
Although rare, infections can occur and are usually managed effectively with antibiotics. Following your surgeon’s aftercare instructions is key to prevention. - Changes in Skin Sensation
Temporary numbness or tingling around the ears is common as nerves adjust post-surgery. In most cases, normal sensation returns over time. - Scarring
Otoplasty scars are typically well-hidden behind the ear or in natural folds, but some patients may experience thicker or more noticeable scars.
Cost of Otoplasty Surgery in Turkey
The cost of otoplasty surgery in Turkey varies based on the complexity of the procedure, the technique used, and the surgeon’s expertise. Prices can also change if otoplasty is combined with other methods. While costs fluctuate, this investment often yields significant emotional and psychological benefits, especially for individuals who have long been self-conscious about their ears.
Otoplasty surgery can also be combined with rhinoplasty or a facelift for a more harmonious facial profile. Learn more about rhinoplasty surgery in Turkey and facelift surgery in Turkey.
Myths About Otoplasty
Despite being a common and safe procedure, otoplasty is surrounded by misconceptions that can make patients hesitant to explore it as an option. Let’s separate fact from fiction in this section:
- Myth 1: Otoplasty is Only for Children
While it’s true that otoplasty is often performed on children to correct ear shape early in life, adults of all ages can benefit from this surgery. Many adults choose otoplasty to boost their confidence and achieve facial harmony. - Myth 2: The Results Look Unnatural
Modern surgical techniques focus on creating natural, symmetrical ear shapes that complement your overall facial features. When performed by an experienced surgeon, results are subtle and balanced—not “pinned back” or artificial-looking. - Myth 3: It’s a Risky or Painful Procedure
Otoplasty is considered a low-risk surgery with minimal discomfort. Most patients report only mild soreness during recovery, easily managed with prescribed medications. - Myth 4: The Scars Will Be Noticeable
Surgeons strategically place incisions behind the ear or within natural folds, making scars virtually invisible once fully healed. - Myth 5: Otoplasty Affects Hearing
This procedure only alters the external shape of the ear and has no impact on hearing ability. Patients often enjoy better self-confidence without any functional side effects. - Myth 6: Recovery Takes Months
While full healing can take several weeks, most patients return to daily activities within a week, making recovery much quicker than many expect.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Otoplasty
How long does the otoplasty procedure take?
The surgery typically lasts 1–3 hours, depending on the complexity of the corrections.
Will I experience pain during or after the surgery?
Anesthesia ensures no pain during surgery. Post-surgery, mild discomfort or soreness is normal and manageable with prescribed medication.
How long does it take to recover from otoplasty?
Most patients return to normal daily activities within a week, but full recovery—including the fading of swelling and bruising—can take 4–6 weeks.
At what age is otoplasty recommended for children?
Otoplasty can be safely performed on children as young as five, as their ear cartilage is usually mature enough by that age.
What happens if I’m not satisfied with the results?
In rare cases, revision surgery may be recommended. Always discuss your concerns with your surgeon to determine the best next steps.
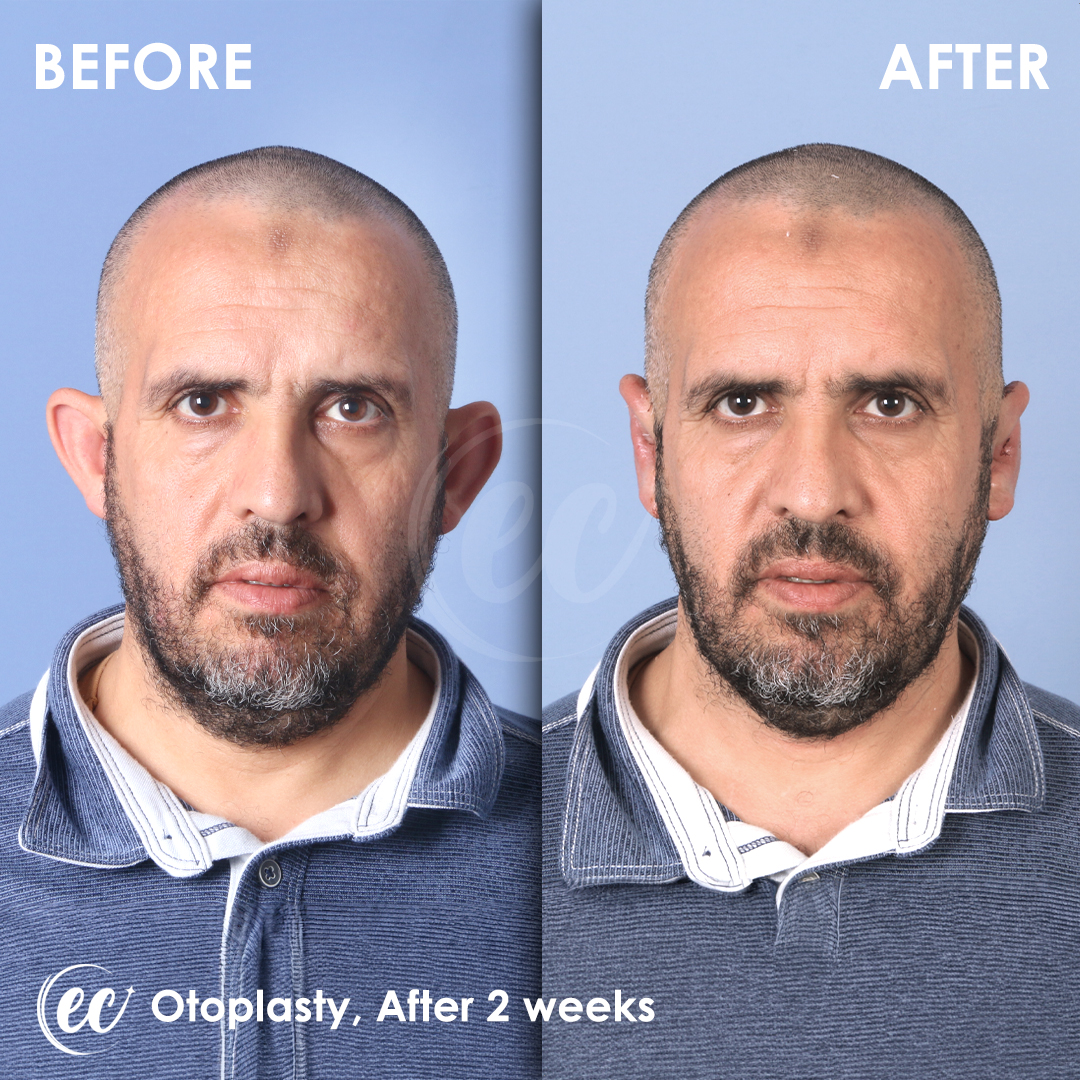
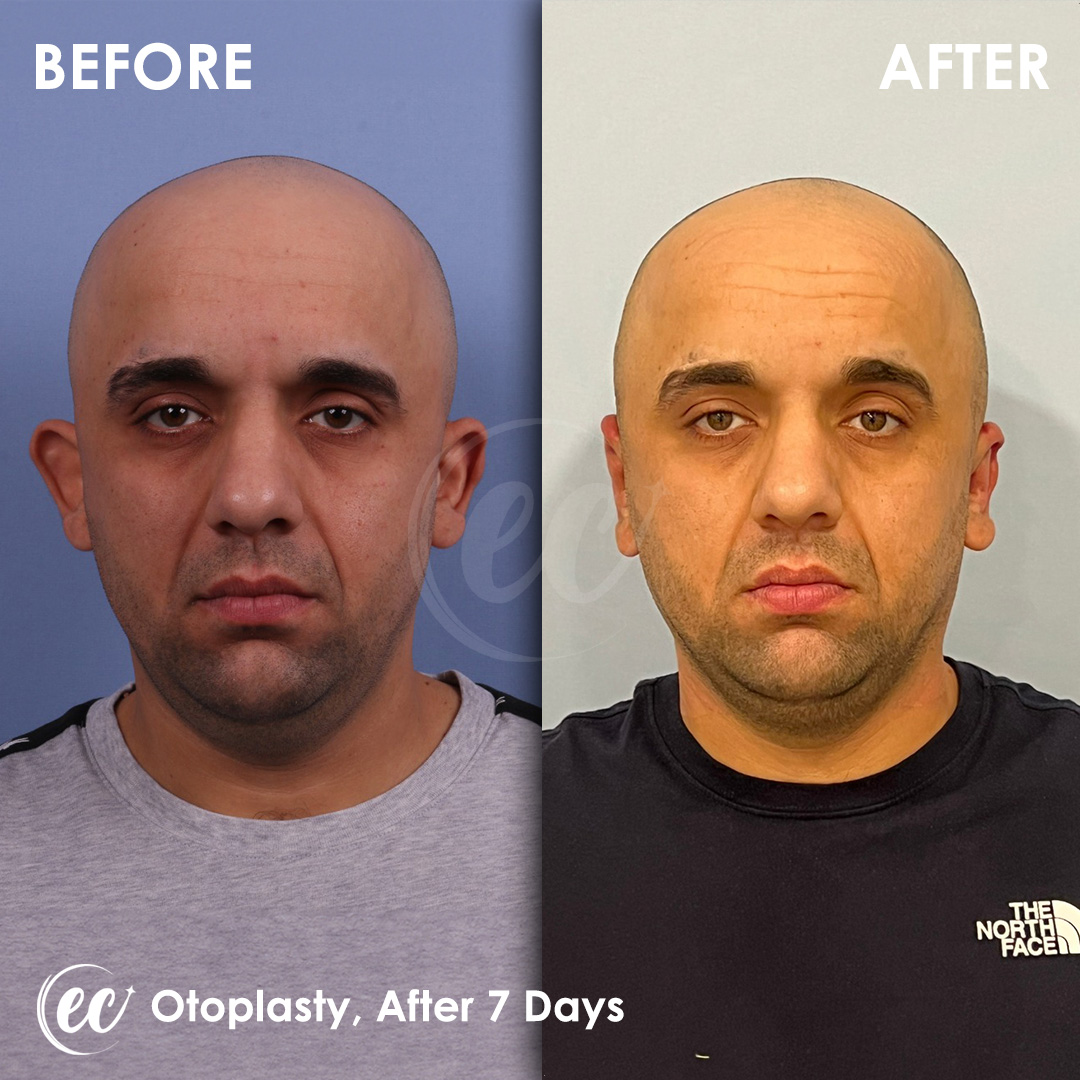
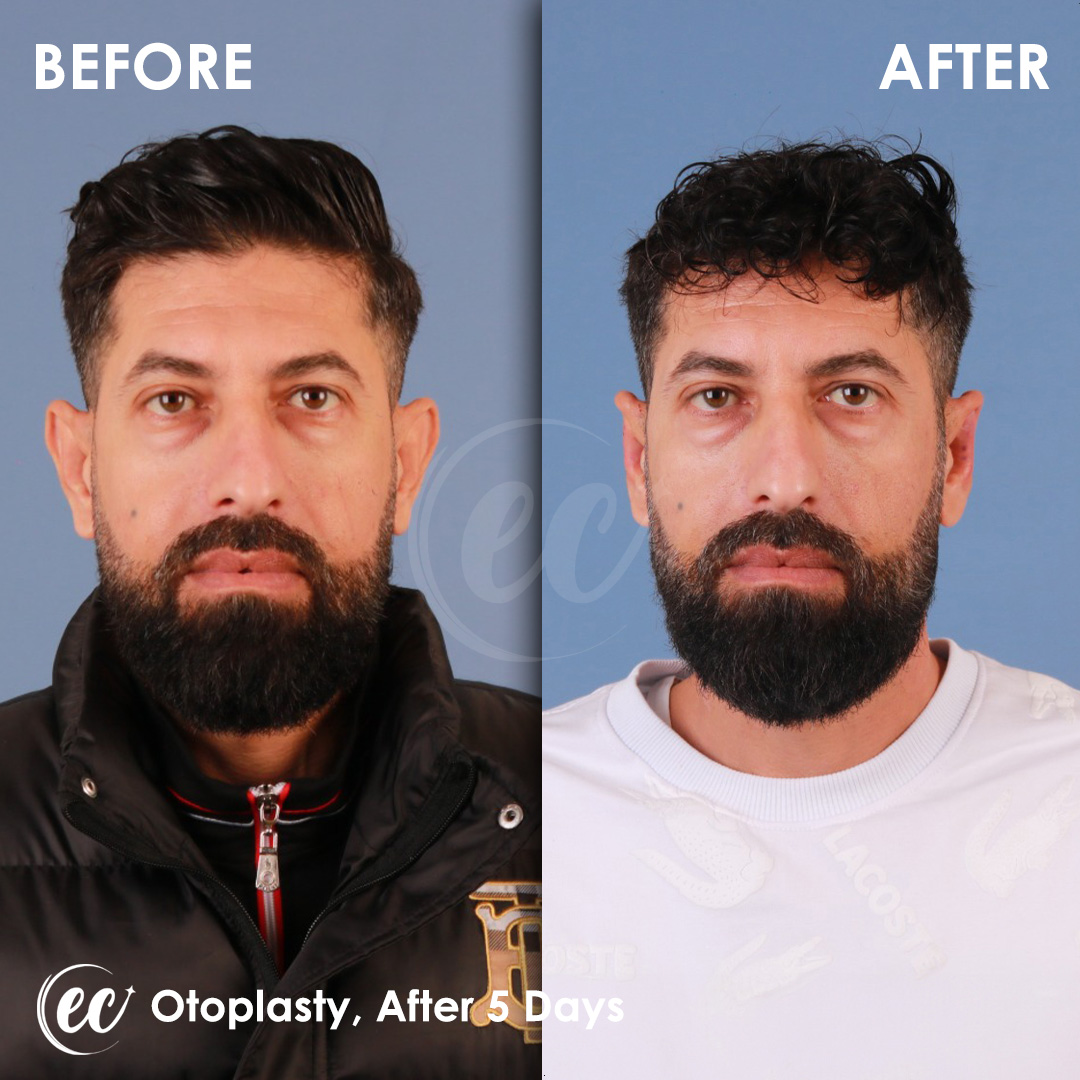
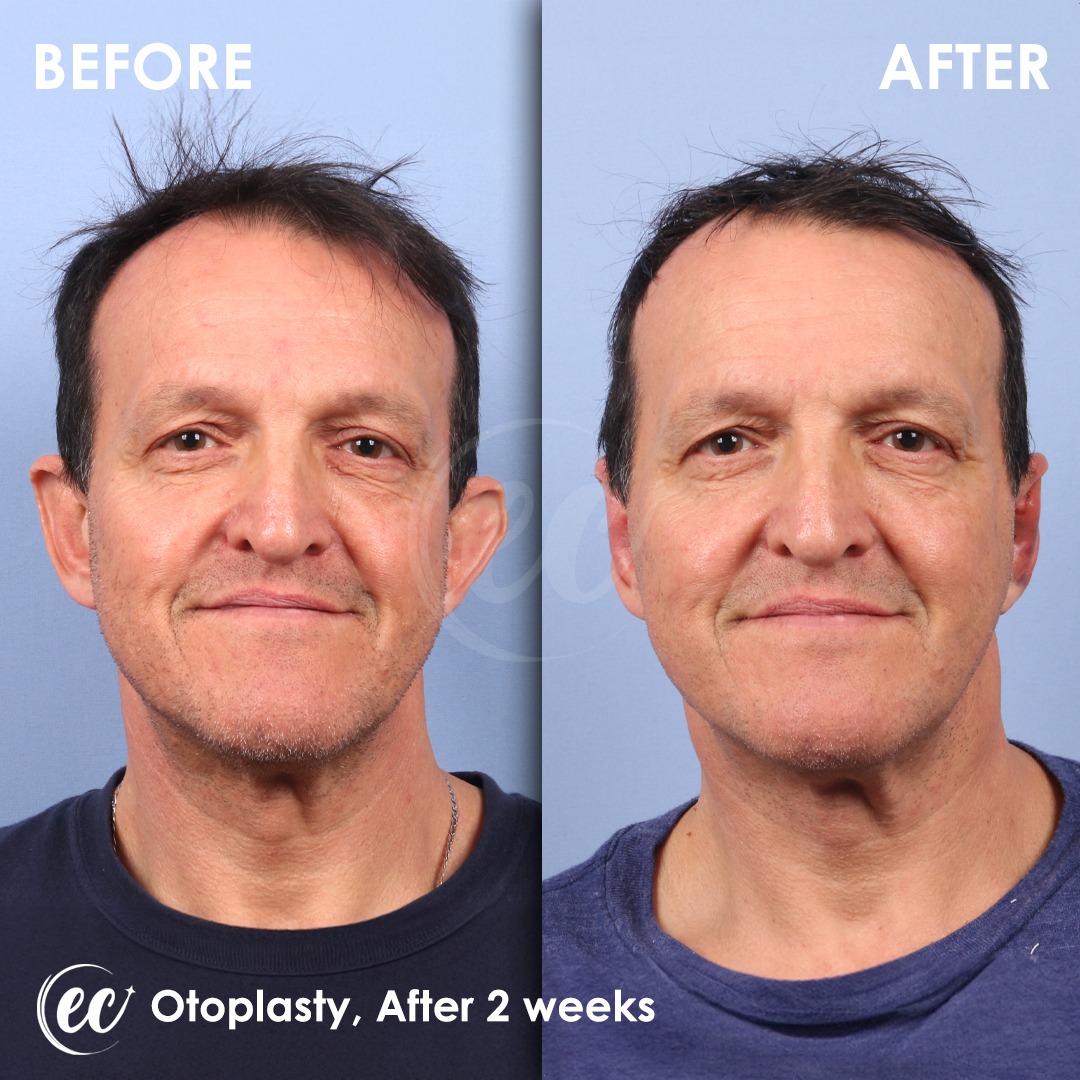
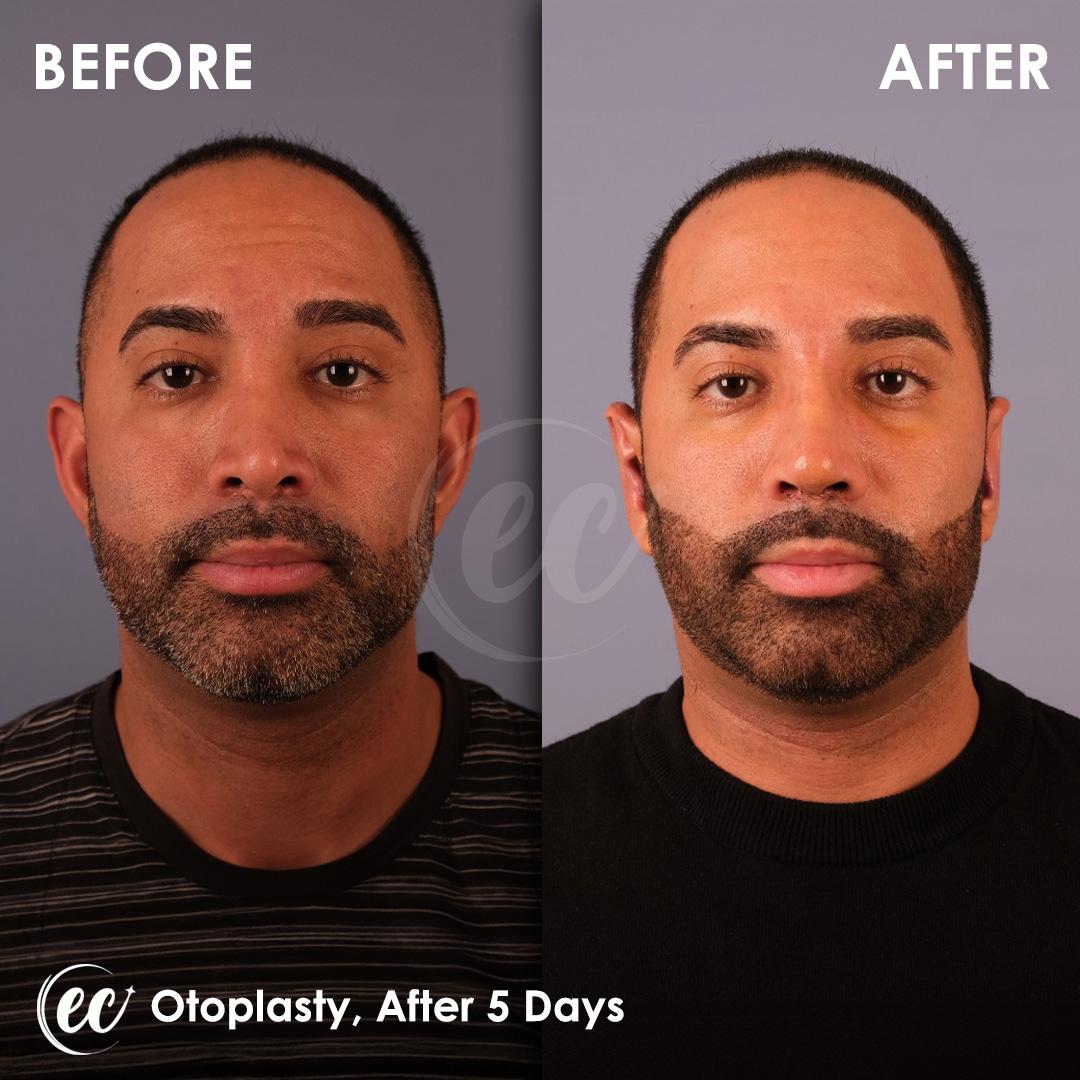
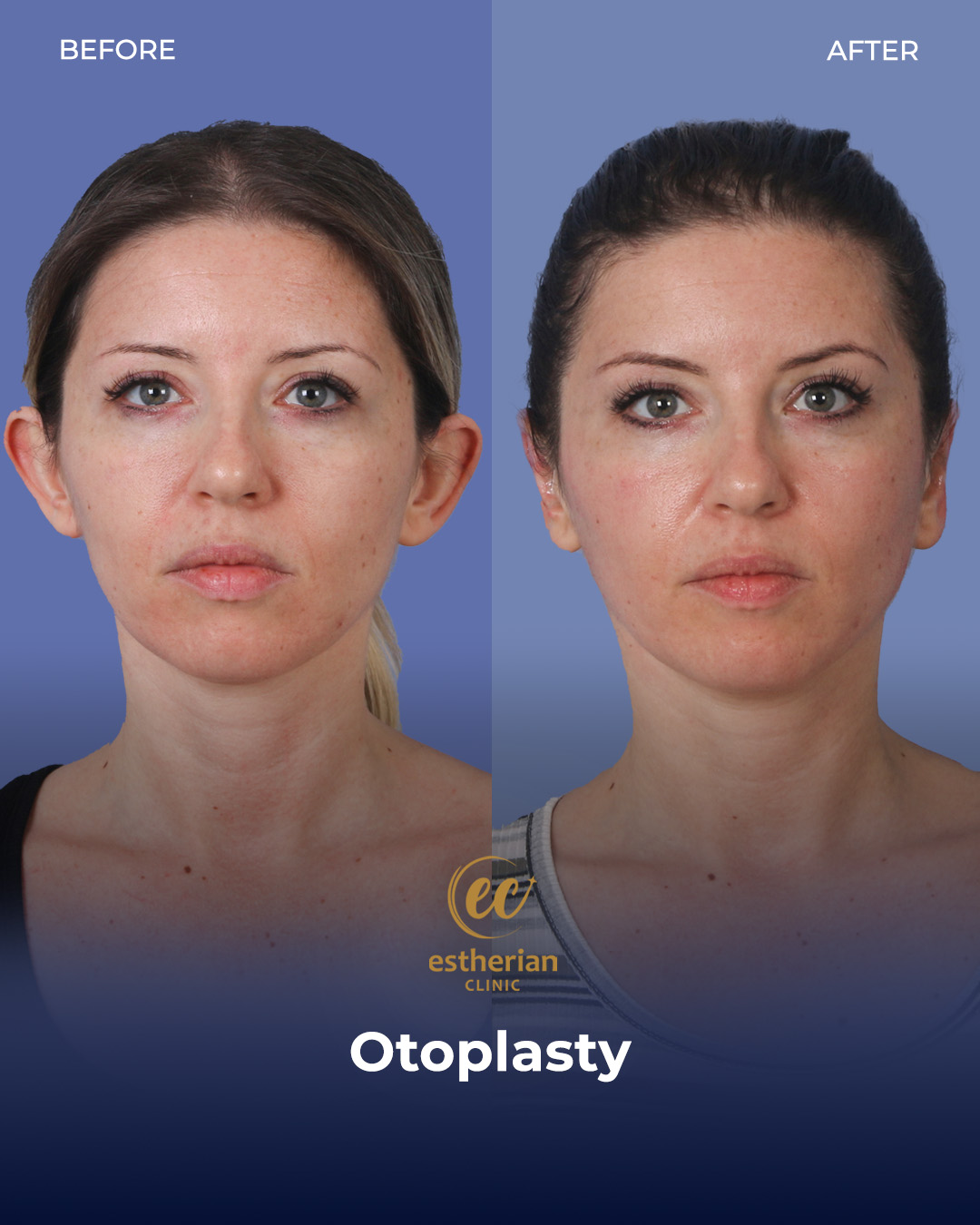
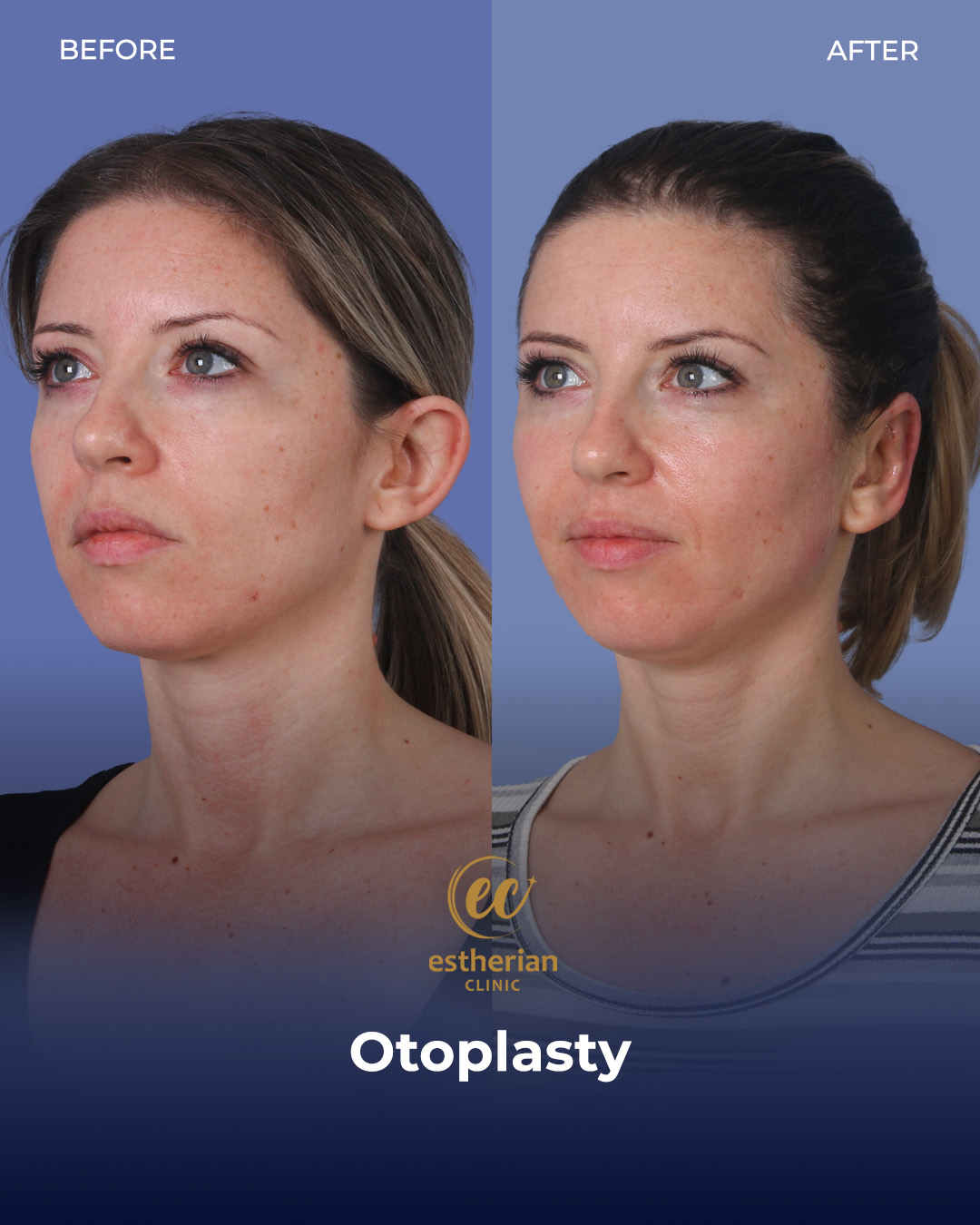
Otoplasty Surgery in Turkey: Before and After
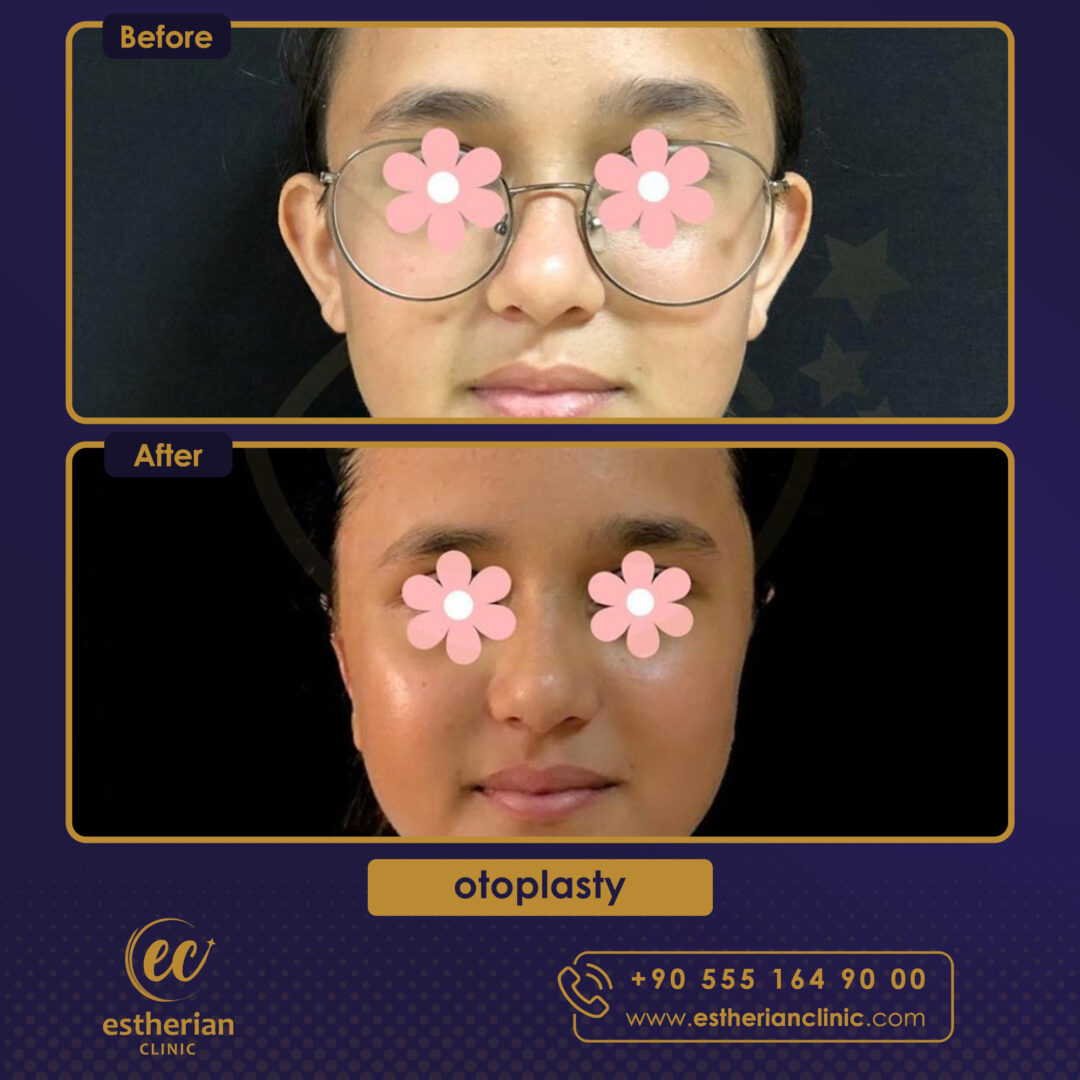
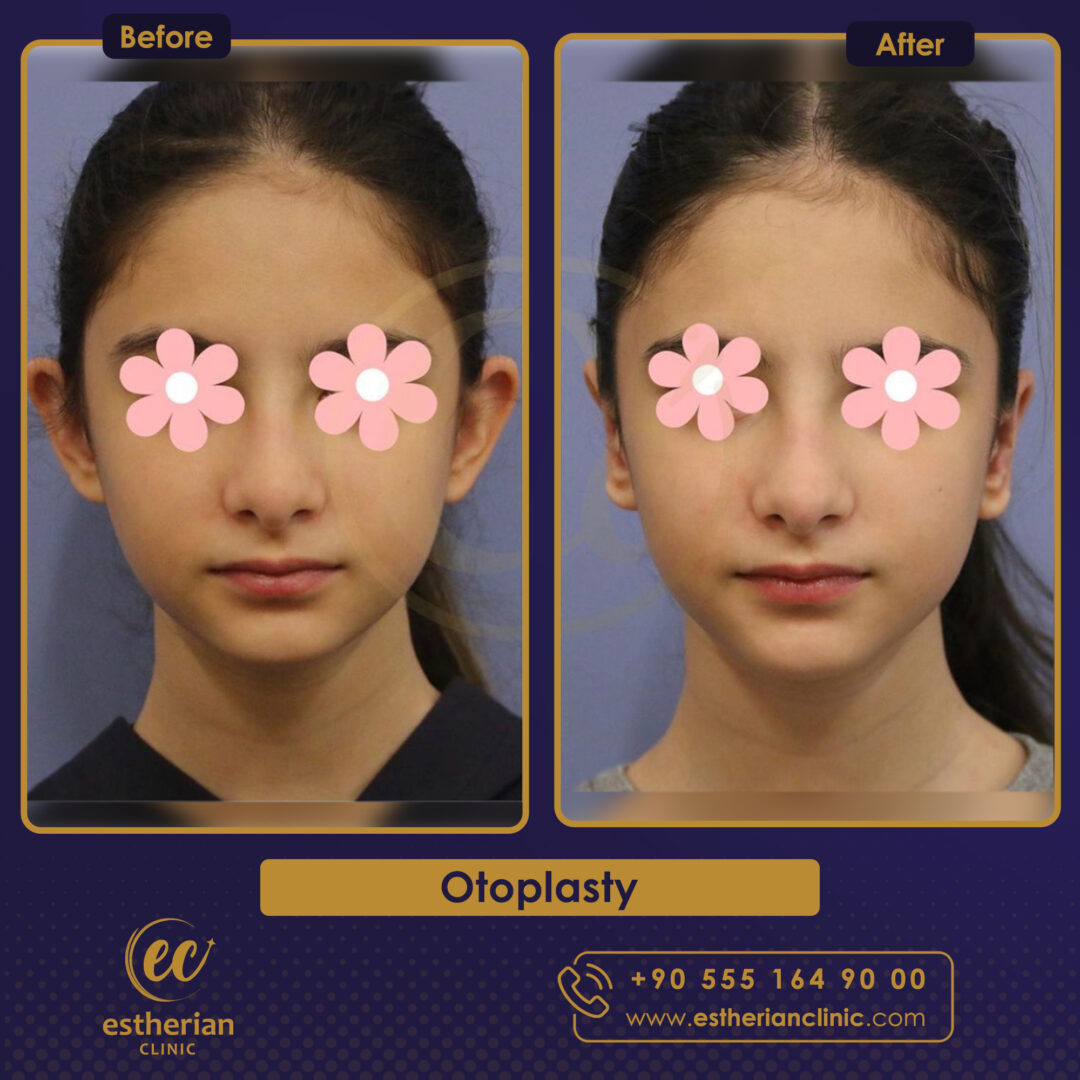
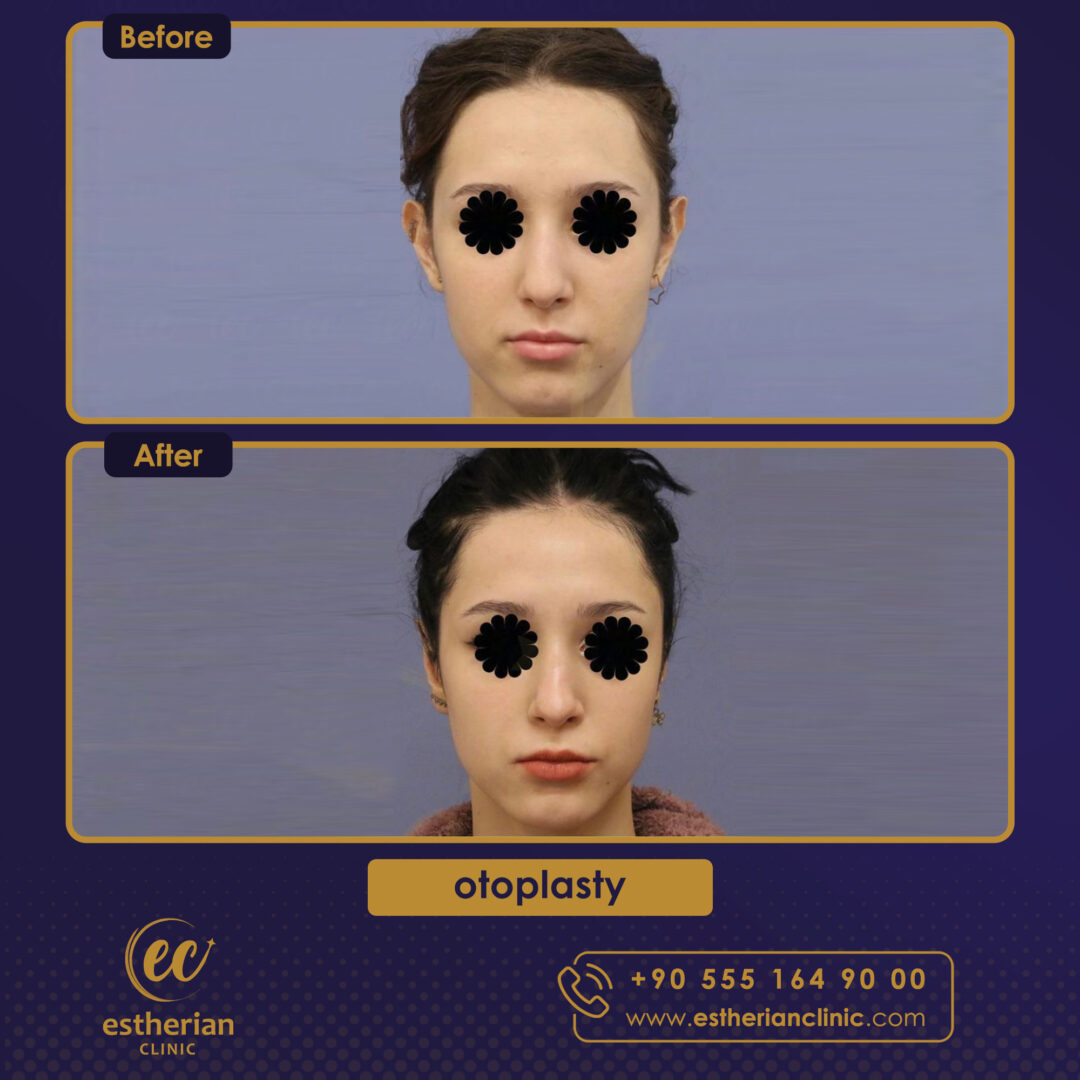



Related Articles About Otoplasty Surgery in Turkey
plasticsurgery.org: “Otoplasty enhances the symmetry and proportion of the ears, creating a natural look.”
realself.com: “Correcting ear concerns can significantly improve confidence in both children and adults.”
Real Otoplasty Transformations – Before and After